
Below we offer 3 tabs to help homebuyers calculate their monthly payments & find a local lender. The first tab calculates adjustable-rate payments, the second tab calculates fixed-rate payments, and the third tab enables homebuyers to view current El Monte jumbo loan rates.
Below is our ARM jumbo mortgage calculator. Click on the other tabs above to switch to the jumbo fixed-rate calculator or to view current El Monte jumbo loan rates. Fixed-rate loans make up the majority of conventional home loans, though adjustable-rate loans are far more common for buyers purchasing with a jumbo or super jumbo mortgage.
If you want to look exclusively at the principal & interest portion of your loan, you can use the following calculator to compare fixed-rates & ARMs side-by-side.
Below is our FRM jumbo mortgage calculator. Click on the other tabs above to switch to the jumbo ARM calculator or to view current El Monte jumbo loan rates.
If you want to look exclusively at the principal & interest portion of your loan, you can use the following calculator to compare fixed-rates, ARMs & I-O only payments side-by-side.
The following table shows current 30-year jumbo mortgage rates available in El Monte. You can use the menus to select other loan durations, alter the loan amount, or change your location.
Purchasing a home is a milestone that signifies readiness and commitment to attain stability. Once you make this decision, you must have a strong financial background with adequate savings and a reliable source of income to pay down your mortgage. On top of this, you must secure the most favorable loan that will suite your needs.
Many large cities in coastal states have expensive property prices. Depending on the home's size and location, a homebuyer might need to take a mortgage that's larger than the usual loan. This is where jumbo mortgages can work for you.
In this guide, we'll define what jumbo mortgages are and how they compare to conventional housing loans. We'll also tackle how jumbo mortgages are funded and how they are commonly structured for consumers. Then we'll rundown differences in the qualification process, loan size and rates, and how it changes in market liquidity.

Jumbo mortgages are home loans that exceed the conforming limit placed by government-sponsored enterprises (GSE). These GSEs buy majority of mortgages and market them to consumers. Jumbo mortgages are also referred to as non-conforming loans. They are commonly used in more expensive cities and locations where house prices are usually higher.
What is a Super Jumbo Mortgage?
Each financial institution has its own definition of the loan amount which shifts a loan from jumbo to super jumbo. In affordable areas of the country this limit can typically be as little as $1,000,000, though the floor is often closer to $2,000,000 or more in expensive parts of the country.
Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac are GSEs which provide liquidity to the national mortgage market by buying mortgages and keeping them in their portfolios. They also package the residential mortgages into mortgage-backed securities (MBS) which are sold to secondary investors. They have limits for the size of the residential mortgages they package into securities. Jumbo mortgages are loans which back home purchases where the amount financed exceeds the conforming mortgage loan limit.
Jumbo does not refer to the size of the house, but rather the amount of the loan. Many coastal properties are highly valued even if they are not physically large dwellings.
According to the Federal Housing Finance Agency (FHFA), as of 2026 the conforming loan limit for single unit homes across the continental United States is $832,750. A ceiling of 150%, which is a $1,249,125 conforming limit, is set in areas where median home values are higher. As stated in the Housing Economic Recovery Act (HERA), the U.S. baseline conforming limit is subject to adjustment every year. This is so GSEs can reflect shifts in the average U.S. home price.
The limit is as follows for 2, 3, and 4-unit homes: $1,066,250, $1,288,800, and $1,601,750. Conforming limits are higher in Alaska, Hawaii, Guam, the U.S. Virgin Islands and other high-cost areas. Loans which exceed these limits are classified as jumbo loans.
See the table below for homes NOT in designated high-cost areas, those within high-cost locations, and other U.S. territories with expensive properties.
| Units | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Continental U.S. Baseline | $832,750 | $1,066,250 | $1,288,800 | $1,601,750 |
| Designated High-cost Areas | $1,249,125 | $1,599,375 | $1,933,200 | $2,402,625 |
| Alaska, Hawaii, Guam & U.S. Virgin Islands | $1,249,125 | $1,599,375 | $1,933,200 | $2,402,625 |
The first row in the table above shows conforming limits for houses within the U.S. continental baseline: Alabama, Arizona, Arkansas, Delaware, Georgia, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Kentucky, Louisiana, Maine, Michigan, Minnesota, Mississippi, Missouri, Montana, Nevada, New Mexico, North Dakota, Ohio, Oklahoma, Rhode Island, South Carolina, South Dakota, Texas, Vermont, Wisconsin, and most other parts of the continental United States.
In the second row, some coastal states are homes to metro areas with higher property prices which qualify as HERA designated high-cost areas.
The third shows conforming limits for the following U.S. locations: Alaska, Guam, Virgin Islands, Washington D.C., and Hawaii.
For a full list of the latest conforming limits in U.S. counties, you may check the FHFA website
Unlike conventional mortgages, jumbo loans generally come with stringent underwriting requirements and meticulous assessment of the applicant's ability to repay. The opportunity to sell a mortgage to GSEs is regarded as a safety net for a lender. This is why financial institutions are more careful when they evaluate a consumer's ability to pay back jumbo mortgages. Ultimately, expect it to cost more than conventional loans due to the larger loan size and the stricter qualifying steps.
While lenders offer varied jumbo loan packages, it's important to know its key differences from conventional loans. This will give you a better idea of what to prepare before you apply for a jumbo loan. From credit scores and interest rates, all the way to documentation and closing costs, here's how jumbo mortgages diverge from conventional loans.

Jumbo: Credit requirements are obviously higher for jumbo loans. Majority of lenders require a FICO score of 700, sometimes even 720 to qualify for a jumbo loan. They usually do not approve applicants with credit scores lower than 660.
Conventional: Ideally, lenders prefer a credit score that's not lower than 680 and favor applicants at 700. But now and then, they may approve consumers with credits scores lower than 600, albeit with higher interest rates.
Jumbo: The added risk linked with non-conforming loans makes lenders increase jumbo interest rates by 1 or 2 percentages points compared to conventional rates. Depending on market conditions, lenders may offer jumbo loan rates that compete with conforming loans. So make sure to shop around to compare. Jumbo loans come in fixed terms or adjustable-rate terms (ARM).
As of May 2020, the table below shows average jumbo mortgage rates at fixed terms and adjustable-rate terms (ARM).
| Product | Interest Rate | APR |
|---|---|---|
| Jumbo 30-Year Fixed | 3.720% | 3.760% |
| Jumbo 15-Year Fixed | 2.990% | 3.010% |
| Jumbo 7/1 ARM | 3.410% | 3.790% |
| Jumbo 5/1 ARM | 3.200% | 3.670% |
Our jumbo mortgages guide offers more in-depth information about loan qualification, payment options & other important background information.
Conventional: Likewise, conventional mortgage rates are lower than jumbo loans. It's also available in fixed and adjustable-rate terms. For both jumbo and conventional loans, take note that rates are generally lower when you secure a shorter term. You're charged a higher rate if you make a low down payment or if you have a lower credit standing.
Below is an example of conventional mortgage rates as of May 2020.
| Product | Interest Rate | APR |
|---|---|---|
| Conventional 15 Year Fixed | 2.875 % | 3.100 % |
| Conventional 30 Year Fixed | 3.375 % | 3.515 % |
| Conventional 5/1 ARM | 3.200% | 3.850% |
| Conventional 7/1 ARM | 3.260% | 3.760% |
Jumbo: Down payments are often stricter with non-conforming mortgages. Most consumers are required to make a 20% down payment, but this differs among lenders. Some may impose a minimum down payment of 30%, 20%, or 15% on a jumbo loan. If you want to make a lower down payment such as 10%, some lenders may allow it. However, to offset the low payment, they often impose a higher interest rate.
Conventional: On average, homebuyers put a 10% down payment on conventional loans. However, paying 20% down payment relieves you of private mortgage insurance (PMI) payments, which vary significantly based on your credit score.

Jumbo: Non-conforming mortgages are appealing to consumers with larger and more complex sources of income. This is why jumbo loans impose more income documentation and paper work on applicants. They undergo strict manual underwriting with an analyst combing through their assets, bank statements, and credit report. You may be asked to produce multiple years of tax returns instead of one to validate your income stream. This is especially required if you are self-employed.
Lenders may also ask for cash reserves to prove you have enough funds in the bank to sustain payments. Your lender may demand up to 18 months' worth of reserve expenses before they approve a jumbo loan. Apart from cash in the bank, lenders consider up to 70% of your retirement account. In other instances, they may even factor in business and gift funds.
Due to the detailed underwriting process, getting a jumbo loan approved may take more than the usual 45 days, and even over 60 days.
Conventional: When it comes to underwriting, applicants are generally required to produce the following documents to secure mortgage approval:
There are also different documentation procedures required for employed applicants and those who are self-employed. On average, it can take between 45 to 60 days for a conventional loan to get approved, especially during high-volume periods.

Jumbo: Expect lenders to look for low debt-to-income ratio (DTI). This is the size of all your debts relative to your monthly income. Majority of lenders require DTI between 38% to 43%. This means your monthly mortgage payments and other loan obligations cannot exceed 43% of your pretax earnings. For instance, if you will make a 10% down payment, aim for a DTI ratio lower than 40%. If you make a larger down payment, some lenders may allow you to qualify with a higher DTI ratio.
Conventional: As for debt-to-income ratio, conventional loan borrowers should have a front-end DTI of 28%, and a back end DTI of 36%, which should not go over 43%. For some applicants carrying student loan debts, they may still qualify even with 50% DTI.
Jumbo: While there are fixed-rate jumbo mortgages, over the years, majority of jumbo loans are structured as adjustable-rate mortgages (ARM). ARMs typically consist of a single digit percent of total mortgages. Common ARM terms come with fixed rate periods of 3, 5, 7, or even 10 years, and then adjust annually after the introductory period. They are referred to as 3/1 ARM, 5/1 ARM, 7/1 ARM and 10/1 ARM.
Fixed-rate vs. ARMs
An adjustable-rate mortgage starts with a low rate and changes periodically when rates reset higher or lower after the introductory period. Fixed-rate mortgages, on the other hand, are locked for the entire life of the loan, regardless of whether interest rates rise or fall over time.
Jumbo ARMs are more appropriate for homebuyers with large savings and a reliable sources of income. Obtaining ARM is risky if rates consistently rise after the introductory period. Therefore, it is crucial for a consumer to be prepared for this possibility with ample funds. And when rates reset lower after the introductory period, they can take advantage of lower payments compared to a fixed-rate loan.
Conventional: Most conforming loans are structured with 30-year fixed payments by lenders. But there are lenders who offer conventional loans with adjustable rates. Many people who refinance their mortgages shift into shorter duration loans with the 15-year being the most popular option.
Jumbo: Closing cost for mortgages range between 3% to 6% of a house's total value. Since loan sizes are larger for jumbo loans, expect to pay higher closing costs compared to conforming loans. For instance, if you have a home valued at $650,000, your closing cost will be somewhere between $19,500 to $39,000.
Conventional: Based on 3% to 6% of your home's total value, a house valued at $250,000 under a conventional loan will have a closing cost between $7,500 to $15,000. Note: You are not required to purchase a property mortgage insurance (PMI) if you have an 80% loan-to-value (LTV) ratio. LTV is the size of your mortgage in relation to the value of your property. Likewise, PMI payments are needed until your LTV is lower than 80%.
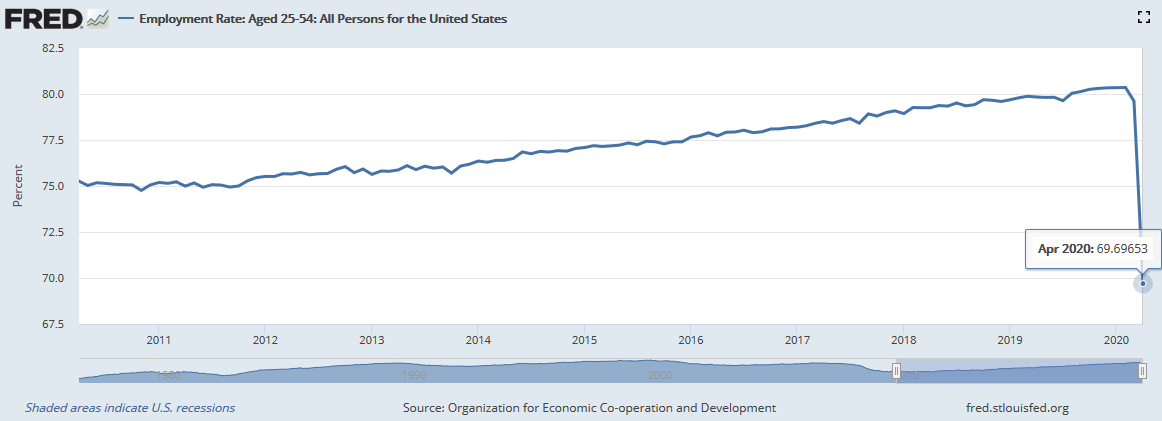
In April 2020, the Wall Street Journal reported that Wells Fargo, America's largest mortgage lender, will only refinance jumbo mortgages for consumers who hold at least $250,000 in liquid assets with the bank.
What does this mean for customers? If you have a jumbo loan with Wells Fargo, you do not have the option to refinance to lower rates unless you keep your money with the bank. This move insures that the lender will not lose more funds from its current investors during the economic downturn.
Conventional loans backed by Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac are still available in the market. However, jumbo mortgages became infrequent because of associated market fluctuations and low demand from investors.
Mortgage lenders were affected as investors try to stay afloat amidst the jobmarket collapse. U.S. stocks dropped when businesses laid off around 701,000 jobs in March 2020 due to the Covid-19 crisis.
The Federal Reserve has supplied the conforming portion of the mortgage market with ample liquidity. More exotic loan structures are less liquid, making working with a mortgage broker more beneficial for homepowers with specific needs for niche products which are less liquid.
Obtaining a jumbo mortgage is an expensive commitment that requires large savings and reliable sources of income compared to conventional loans. Since jumbo mortgages are not backed by government-sponsored enterprises, they require strong creditworthiness from investors.
Depending on your location, conforming limits may be higher compared to other areas. Make sure to check your location's conforming limit to see if you might need to take a jumbo loan.
Be prepared to have your financial background scrutinized by your lender. Finally, don't forget to improve your credit score before you apply for a jumbo loan.
Read our jumbo mortgage guide for thorough information on loan requirements, payment options, and other important details.
Explore conventional mortgages, FHA loans, USDA loans, and VA loans to find out which option is right for you.
Check your options with a trusted El Monte lender.
Answer a few questions below and connect with a lender who can help you save today!